India’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation has eased significantly to an estimated range of 0.4% to 0.6% in October 2025, according to a report released by the Bank of Baroda (BoB). This marks a continuation of the downward trend observed in recent months, with September’s CPI inflation already at an eight-year low of 1.54%, down from 2.07% in August. The sharp moderation is attributed to declining prices of essential commodities, a favorable base effect, and the government’s Goods and Services Tax (GST) rate rationalisation.
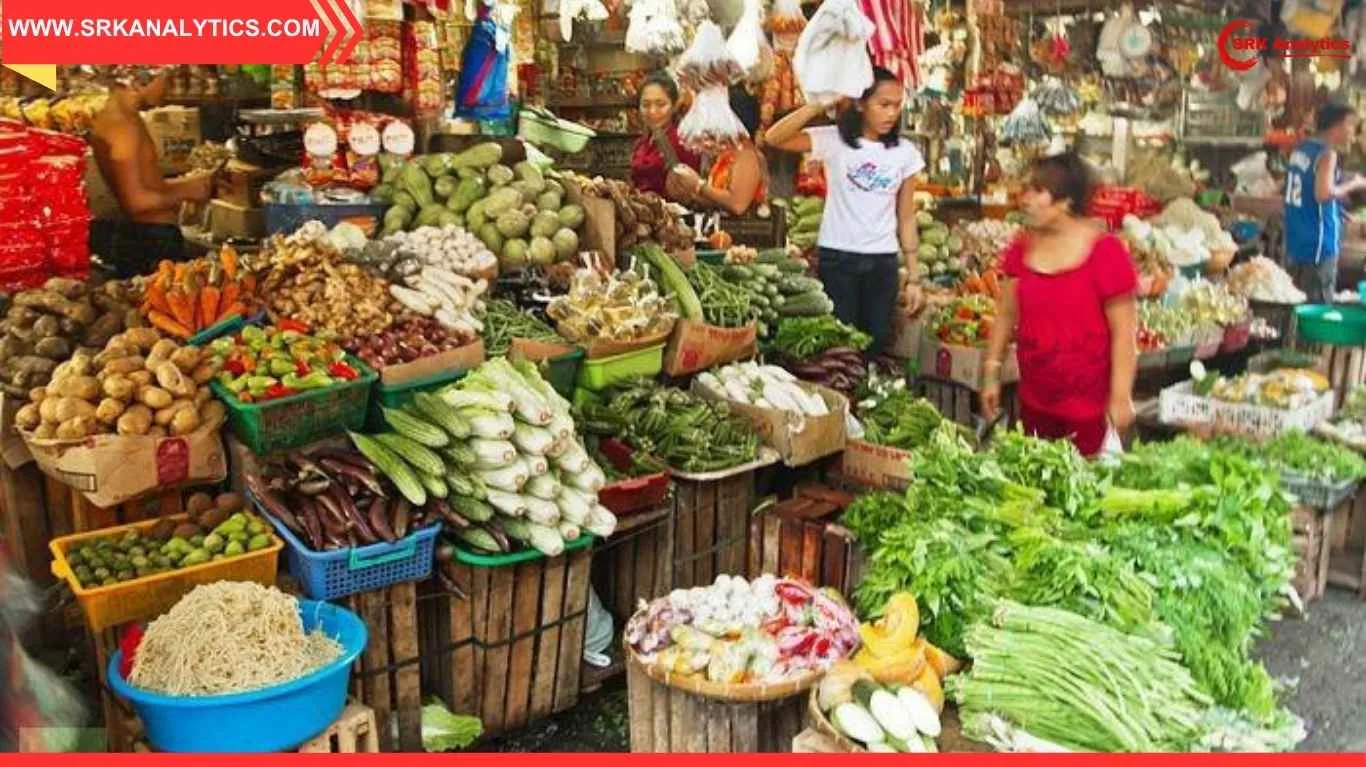
BoB’s economists highlighted that the deflationary trend in food prices—particularly vegetables like tomatoes, onions, and potatoes—played a pivotal role in cooling inflation. The report also noted that global commodity prices have softened, and supply conditions have remained stable, contributing to a benign inflation outlook.
📊 Key Drivers Behind October’s CPI Inflation Decline
| Factor | Impact on Inflation Rate |
|---|---|
| Food Price Deflation | Year-on-year food inflation at –2.28% |
| Global Commodity Price Easing | Lower input costs across sectors |
| GST Rate Rationalisation | Reduced indirect tax burden |
| Favorable Base Effect | Statistical moderation from high prior-year base |
| Mandi Arrivals | Increased supply of vegetables |
The BoB Essential Commodities Index (BoB ECI) contracted by 3.6% in October and further by 3.8% in early November, reinforcing the trend.
📈 CPI Inflation Trend Over Recent Months
| Month | CPI Inflation (%) | Food Inflation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| August 2025 | 2.07 | –1.12 |
| September 2025 | 1.54 | –2.28 |
| October 2025 | 0.4–0.6 (est.) | –2.5 to –3.0 (est.) |
This trajectory reflects one of the steepest disinflationary phases in India’s recent economic history.
🗣️ Expert Commentary on Inflation Outlook
| Stakeholder | Commentary Summary |
|---|---|
| Aditi Gupta, BoB Economist | “Vegetable deflation and strong mandi arrivals are key.” |
| RBI Policy Analysts | “Benign inflation supports accommodative stance.” |
| Retail Sector Leaders | “Lower inflation boosts consumer sentiment.” |
| Global Investors | “India’s macro stability is increasingly attractive.” |
The Reserve Bank of India is expected to maintain its current policy rates amid the favorable inflation environment.
📌 Strategic Implications for Economy and Policy
| Area | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Monetary Policy | Scope for rate stability or future easing |
| Fiscal Planning | Reduced subsidy burden and better budget control |
| Consumer Demand | Higher purchasing power and retail growth |
| Investment Sentiment | Improved outlook for equity and bond markets |
The inflation moderation strengthens India’s macroeconomic fundamentals ahead of the Union Budget 2026.
📉 Sectoral Impact of Lower CPI Inflation
| Sector | Benefit from Inflation Easing | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| FMCG | Lower input costs, better margins | Price stability supports volume growth |
| Agriculture | Mixed impact due to falling vegetable prices | Farmers may face margin pressure |
| Retail | Boost in consumer spending | Festive season demand likely to rise |
| Infrastructure | Lower material costs | Project execution may accelerate |
While consumers benefit, producers in deflation-hit sectors may require support.
📌 Conclusion
India’s CPI inflation easing to a range of 0.4–0.6% in October 2025 marks a significant milestone in the country’s economic recovery. Driven by falling food and commodity prices, stable supply chains, and prudent fiscal measures, the inflation outlook remains benign. As policymakers and investors assess the implications, the focus will shift to sustaining growth momentum while ensuring price stability. With the RBI’s next monetary policy review on the horizon, all eyes will be on how this inflation data shapes future decisions.
Disclaimer: This article is based on publicly available economic reports, financial data, and verified media coverage. It is intended for informational and editorial purposes only and does not constitute financial or investment advice.